We will use Terraform to build an AWS RDS PostgreSQL database which uses the default VNC.
All the following operations have been cimpleted on a Centos VM.
If the following git repository hasn’t been download already then execute the following:
cd ~/git git clone https://github.com/paulhhallam/AWS-RDS-PostgreSQL.git cd AWS-RDS-PostgreSQL
The files in this terraform configuration are :
aws.tf secret.tf RDS-Postgres.tf
aws.tf
- Define the region
- Define the instance type (t2.micro is free tier eligible)
- List the AWS AMI’s to use (Centos)
- Name of the default RDS subnet group
variable "region" {
default = "us-east-1"
}
variable "aws_instance_type" {
default = "t2.micro"
}
variable "amis" {
type = "map"
default = {
"us-east-1" = "ami-b374d5a5"
"us-east-2" = "ami-5e8bb23b"
"us-west-2" = "ami-4b32be2b"
}
}
variable "rds_public_subnet_group" {
default = "default"
description = "The group name used by the RDS launch wizard."
}
secret.tf
Defnie the variables that will be populated with the AWS access keys
variable "access_key" {}
variable "secret_key" {}
RDS-Postgres.tf
- Define the provider (AWS), the access keys variables, the region and the terraform version.
- Get the default VPC id from AWS
- Define the security group allowing input and output from anywhere.
- Create the RDS PostgreSQL database
provider "aws" {
access_key = "${var.access_key}"
secret_key = "${var.secret_key}"
region = "${var.region}"
version = "~> 1.30"
}
# Get the default VPC id
data "aws_vpc" "default" {
default = true
}
resource "aws_security_group" "RDSdbs1" {
name = "RDSdbs1"
description = "RDS database servers (terraform-managed)"
vpc_id = "${data.aws_vpc.default.id}"
# Anyone in
ingress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
# Allow all outbound traffic.
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
resource "aws_db_instance" "RDSpgdb1" {
allocated_storage = 5
backup_retention_period = 0
instance_class = "db.t2.small"
password = "Password1"
username = "DBUser"
final_snapshot_identifier = "DEMODB2"
multi_az = false
publicly_accessible = true
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.RDSdbs1.id}"]
engine = "postgres"
engine_version = "9.5.4"
identifier = "pgdb1"
name = "pgdb1"
# storage_type = "gp2"
# password = "${trimspace(file("${path.module}/secrets/mydb1-password.txt"))}"
port = 5432
# storage_encrypted = true # not required for a test
}
output "EndPoint" {
value = "${aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1.endpoint}"
}
output "Identifier" {
value = "${aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1.identifier}"
}
output "DB_Name" {
value = "${aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1.name}"
}
output "Port" {
value = "${aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1.port}"
}
output "MasterUsername" {
value = "${aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1.username}"
}
Execute
$ terraform init -var-file="/home/devopsdba/Documents/...../SECRET_variables.auto.tfvars"
:
$ terraform apply -var-file="/home/devopsdba/Documents/...../SECRET_variables.auto.tfvars"
data.aws_vpc.default: Refreshing state...
:
Plan: 2 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value:
Entering YES will produce:
aws_security_group.RDSdbs1: Creating...
:
Apply complete! Resources: 2 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
DB_Name = pgdb1
EndPoint = pgdb1.cdxnntiaphrn.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:5432
Identifier = pgdb1
MasterUsername = DBUser
Port = 5432
$
We can now start pgAdmin and test the database.
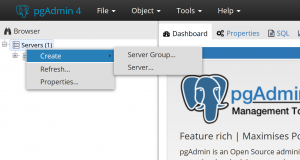
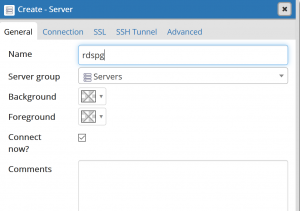
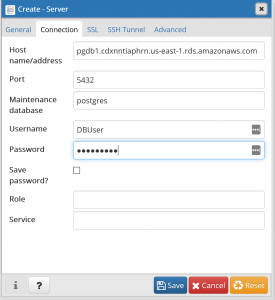
Select “Save”
We will now be presented with the PgAdmin dashboard.
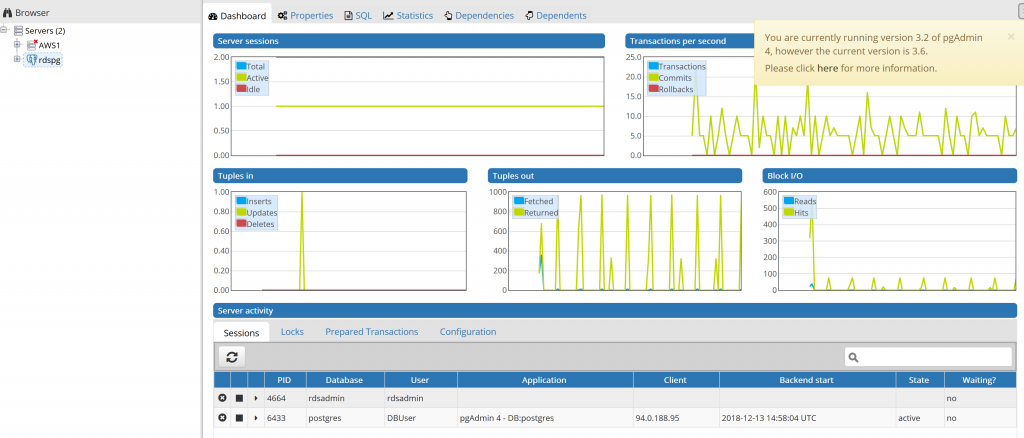
When complete we can destroy the environment with the command:
$ terraform destroy -var-file=”/home/devopsdba/Documents/……/SECRET_variables.auto.tfvars”
data.aws_vpc.default: Refreshing state…
aws_security_group.RDSdbs1: Refreshing state… (ID: sg-0c88b7f606a0c3f03)
aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1: Refreshing state… (ID: pgdb1)
An execution plan has been generated and is shown below.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
- destroy
Terraform will perform the following actions:
- aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1
- aws_security_group.RDSdbs1
Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 2 to destroy.
Do you really want to destroy all resources?
Terraform will destroy all your managed infrastructure, as shown above.
There is no undo. Only ‘yes’ will be accepted to confirm.
Enter a value: yes
aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1: Destroying… (ID: pgdb1)
aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1: Still destroying… (ID: pgdb1, 10s elapsed)
:
- aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1: Still destroying… (ID: pgdb1, 7m50s elapsed)
- aws_db_instance.RDSpgdb1: Destruction complete after 7m55s
- aws_security_group.RDSdbs1: Destroying… (ID: sg-0c88b7f606a0c3f03)
- aws_security_group.RDSdbs1: Destruction complete after 1s
- Destroy complete! Resources: 2 destroyed.
- $